Love is an incredibly complex and multifaceted emotion that can be experienced in countless forms between men and women. Each type of love offers a unique perspective on human connection, and understanding these various types of love can significantly enhance the quality of our relationships. Whether it’s the initial rush of infatuation or the enduring bond that develops over time, love plays an essential role in shaping our lives. In fact, there are different types of love that manifest in a variety of ways, each with its own distinct qualities and dynamics. By understanding the different types of love, we can better navigate our emotional connections, fostering healthier and more meaningful relationships.
This article explores the different types of love between men and women. We will discuss their significance and how they show up in real life. Examples of romantic love, companionate love, and unconditional love will be covered, along with the complexities of falling in love. Understanding these types of love helps us see the layers of affection we experience, deepening our understanding of ourselves and others. Whether you’re in a relationship or curious about human emotions, this article will guide you through the different types of love and offer insights into these connections.
We’ll look at how falling in love can manifest in both fleeting and lasting forms, and how these relationships evolve. From passionate love to committed love, every type of love plays an important role in the way we form bonds with those around us. So, if you’re curious about the various expressions of love, or seeking to understand how romantic connections develop over time, read on.
1. Passionate Love
Passionate love, also known as romantic love, is one of the most intense forms of love. It is marked by strong emotions, intense physical attraction, and a deep desire to be with another person. This love is most common in the early stages of a relationship, when both partners are excited by the novelty of being in love. Passionate love brings intense emotions, and individuals often feel a strong urge to be near their partner, thinking about them and wanting their company.
Psychologist Elaine Hatfield describes passionate love as “a state of intense longing for union with another.” This love can be all-consuming, causing emotional highs and lows as individuals idealize their partner and seek reciprocation. Falling in love and feeling the rush of passion is one of the most exciting aspects of human connection. These types of love are defined by emotional intensity and can lead to euphoria, where everything else fades away when you’re with the one you adore.
As the relationship progresses, the passionate love often evolves, but in its early stages, it is full of excitement and romantic energy. This type of love can create a magnetic attraction that draws two people together, fostering a connection that feels electric. The infatuation that accompanies passionate love is sometimes referred to as the “honeymoon phase,” where both partners are infatuated with one another and experience a rush of emotions with each interaction.
Example: Imagine a couple that has just started dating and finds themselves unable to stop thinking about each other. They constantly yearn to be together, feeling a surge of excitement at every touch, and even a simple glance from their partner sparks a feeling of joy. This is the essence of falling in love, a feeling that can be both thrilling and intoxicating.
2. Companionate Love
Various types of love include companionate love, which is one of the most profound and enduring forms. It is characterized by deep affection, emotional intimacy, and a strong sense of commitment. Unlike passionate love, which is marked by intense physical attraction and excitement, companionate love is defined by a stable, lasting connection built on mutual respect and understanding. This love grows over time, as partners share experiences, support each other through challenges, and form a deep emotional bond. While the initial passion may fade, the love in companionate relationships remains strong, grounded in companionship and trust.
Robert Sternberg’s triangular theory of love explains that companionate love includes intimacy and commitment, but lacks passion. This love is common in long-term marriages or relationships after the initial infatuation fades. The emotional connection remains strong. Over time, partners develop a deep sense of partnership, built on shared values and experiences. Their love becomes about supporting each other through everything.
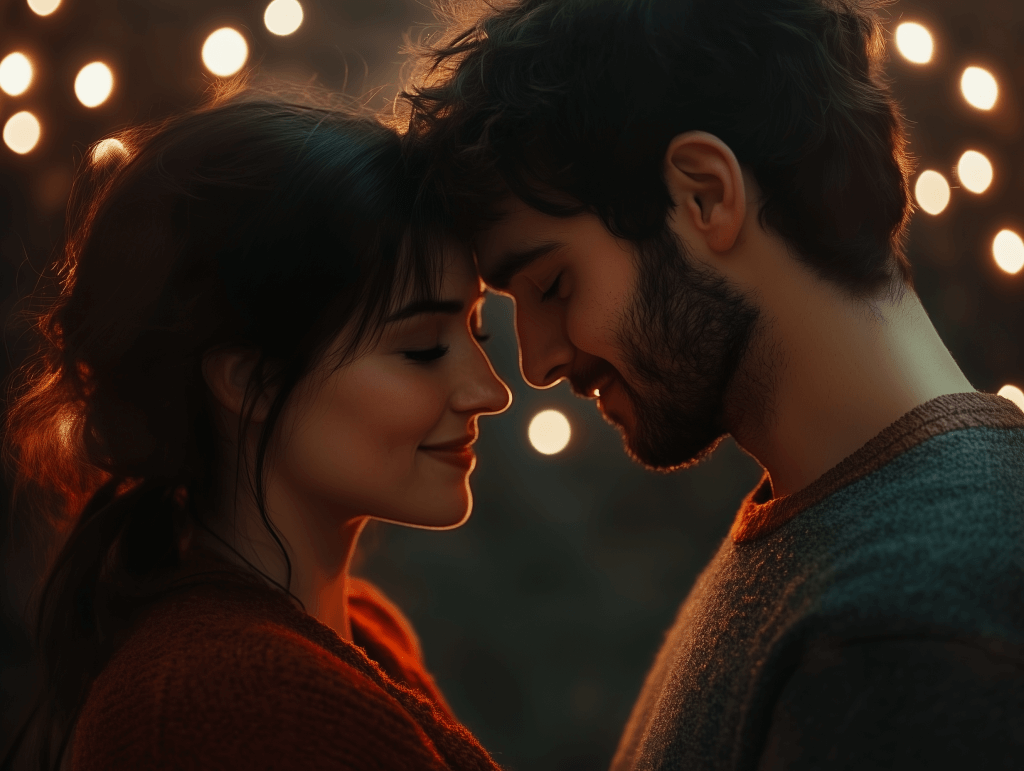

In companionate love, the bond between partners grows stronger as they face life’s challenges together. This makes their relationship unshakable. The emotional intimacy and commitment in this type of love create stability and security. It becomes one of the most fulfilling and meaningful connections people can have.
Example: Consider an elderly couple who have been married for decades. While they may no longer experience the fiery passion of their youth, they share a deep emotional bond that has grown and strengthened over the years. They understand one another’s needs without words and offer unwavering support, especially in times of difficulty. This is the embodiment of companionate love—a profound connection that transcends physical attraction and is built on the foundation of trust, respect, and shared history.
3. Infatuated Love
Infatuated love is one of the various types of love, driven by passion alone, without intimacy or commitment. It often involves intense physical attraction and an idealized view of the other person. There is little emotional connection in this type of love. Infatuation can be exciting but is usually short-lived. It relies on surface-level attraction rather than deep understanding. Though people may confuse it with true love, infatuation lacks emotional depth and lasting commitment.
According to Robert Sternberg’s triangular theory of love, infatuated love is one of the seven forms of love. Sternberg notes that it can arise suddenly, like a rush of emotions, but it often fades just as quickly if it is not supported by the development of intimacy or commitment. Infatuated love is all about the intense rush of desire, which, while exhilarating, can quickly dissipate if there is no emotional depth or dedication to sustaining the relationship.
Infatuated love is often shallow and based on fantasies about the person. It lacks a true understanding of who they are. Physical attraction and the desire for romance drive it. Without trust or companionship, it’s hard to sustain. If intimacy or commitment doesn’t develop, it may fade quickly after the initial phase.
Example: Imagine someone who develops a strong crush on a celebrity or a stranger, feeling an overwhelming attraction to them without really knowing them on a personal level. The attraction may feel all-consuming at first, but since it lacks deeper intimacy or commitment, it is unlikely to last. This is an example of infatuated love—an intense, passionate attraction that, while exciting, may fade as quickly as it appeared.
4. Empty Love
Empty love is characterized by commitment without passion or intimacy. In this type of love, the relationship persists due to a sense of duty or obligation, but there is little emotional connection or physical attraction. Empty love can occur in long-term relationships where the initial spark has faded, and efforts to maintain intimacy have diminished.
Sternberg suggests that empty love can mark the end of a fading relationship. It can also be the starting point in arranged marriages. In such cases, commitment comes first, followed by intimacy and passion.
Example: A couple stays together only for their children or due to societal pressure. They lack emotional closeness and physical desire.
5. Romantic Love
Romantic love combines elements of both passion and intimacy. It involves a deep emotional connection and physical attraction without necessarily including a long-term commitment. This type of love is often celebrated in literature and art, highlighting the bliss and challenges of such relationships.
Sternberg’s triangular theory describes romantic love as a mix of intimacy and passion. In this type of love, individuals feel connected and attracted to each other. However, they may not have made future plans together.
Example: Two people meet during a vacation and share a profound connection and attraction, fully aware that their relationship is temporary and will end when the vacation concludes.
6. Fatuous Love
Various types of love include fatuous love, which is characterized by passion and commitment without intimacy. This type of love often leads to whirlwind romances and quick commitments without a deep emotional connection. Such relationships may be unstable due to the lack of a solid foundation of intimacy.
In Sternberg’s model, fatuous love arises when individuals commit based on passion alone, without truly knowing each other.
Example: A couple meets and decides to get married within a few weeks, driven by intense attraction but without taking the time to build a deeper connection.
7. Consummate Love
Consummate love is considered the complete form of love, encompassing passion, intimacy, and commitment. It represents the ideal relationship where partners share a deep emotional bond, physical attraction, and a commitment to maintaining the relationship over time. Achieving and sustaining consummate love requires effort, communication, and mutual respect.
Sternberg emphasizes that while consummate love is the most fulfilling, it is also the most challenging to maintain, as it requires balancing all three components of love.
8. Unconditional Love
Unconditional love is the most selfless form of love. One partner loves the other without expecting anything in return. This love is often seen in parental love, where a parent always loves their child, no matter what. In romantic relationships, unconditional love appears when one partner accepts the other’s flaws without trying to change them.
This type of love does not rely on conditions or external factors and is often seen as the purest form of affection. While it can be hard to achieve, when it is present, it provides a stable foundation for a lasting relationship.
Example: A partner who supports their significant other through difficult times, such as illness or financial struggles, without judgment or hesitation, is showing unconditional love.
9. Limerence (Obsessive Love)
Limerence refers to an intense and obsessive form of love, where one person constantly thinks about another and feels consumed by the desire to be reciprocated. This type of love is often marked by intrusive thoughts, constant longing, and emotional dependency on the other person. Limerence can feel overwhelming and often leads to anxiety and uncertainty if the feelings are not returned or reciprocated.
Psychologist Dorothy Tennov, who coined the term “limerence,” describes it as “an involuntary cognitive and emotional state in which a person feels infatuated with another person.”
Example: A person who checks their phone often for messages is likely experiencing limerence. They may obsess over someone they’ve just met, hoping for a romantic connection.
Conclusion
Various types of love are a crucial part of the human experience. They take many forms: passionate romantic love, lasting companionate love, and selfless unconditional love. Each type plays an important role in relationships. These forms of love may change over time or vary between individuals, but respect, care, and connection are always present.
Falling in love is a unique and complex journey. Understanding the various types of love helps us appreciate human relationships. Each form of love offers valuable lessons, deepening our understanding of ourselves and others.